
Cut Costs and Gain Insights with Free VPC IP Address Manager
As you know, AWS now charges for every public IPv4 address you use. At $0.005 per hour, even a single address can cost you around $44 per year. But fear not! This guide will show you how to easily map all your IPv4 addresses in one place and make informed decisions to optimize your costs.
Step 1: Access VPC IP Address Manager
- Navigate to the Amazon VPC Console and search for “VPC IP Address Manager.”
- Click “Create IPAM” to begin.
Step 2: Configure IPAM Settings
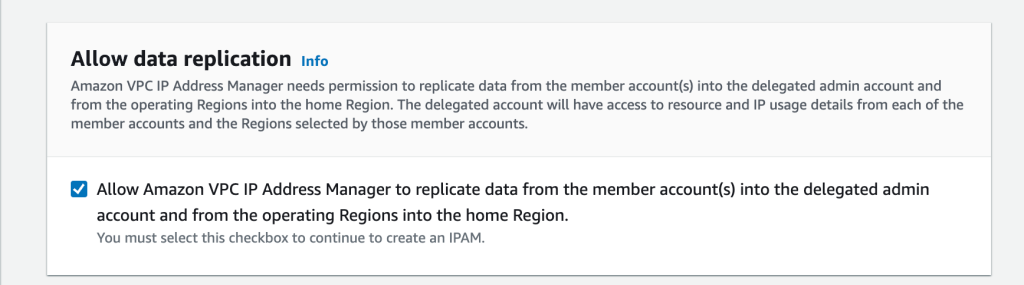
- Check the box “Allow Amazon VPC IP Address Manager to replicate data…” This ensures all your IP addresses across regions are included.
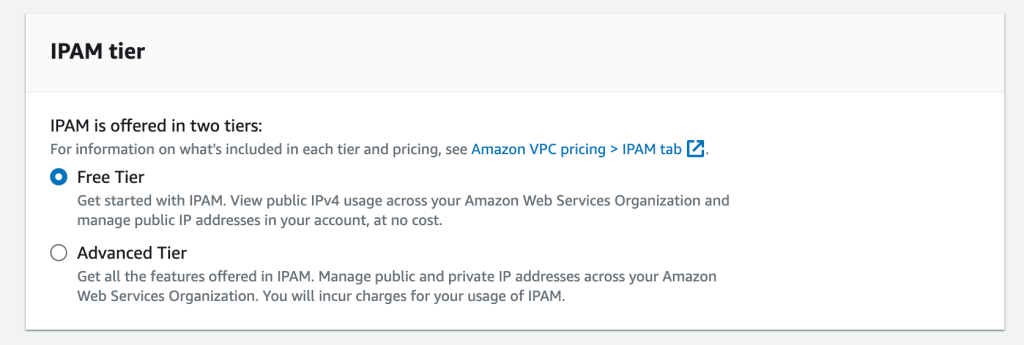
2. Select “Free Tier” to avoid additional charges.
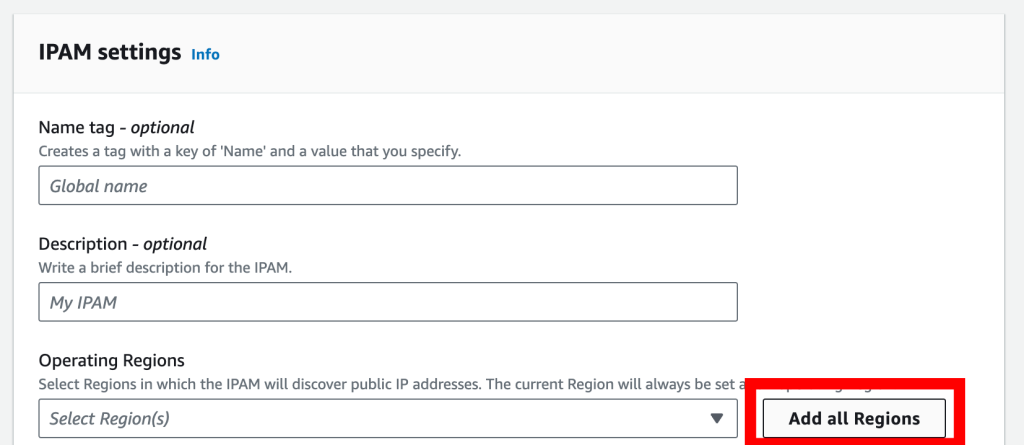
3. Name & Description: Optional, but helpful for organization.
4. Regions: Click “Add all Regions” to capture all your IPv4 addresses.
5. Click “Create IPAM” to finalize.
Step 3: Analyze Your Resource Usage
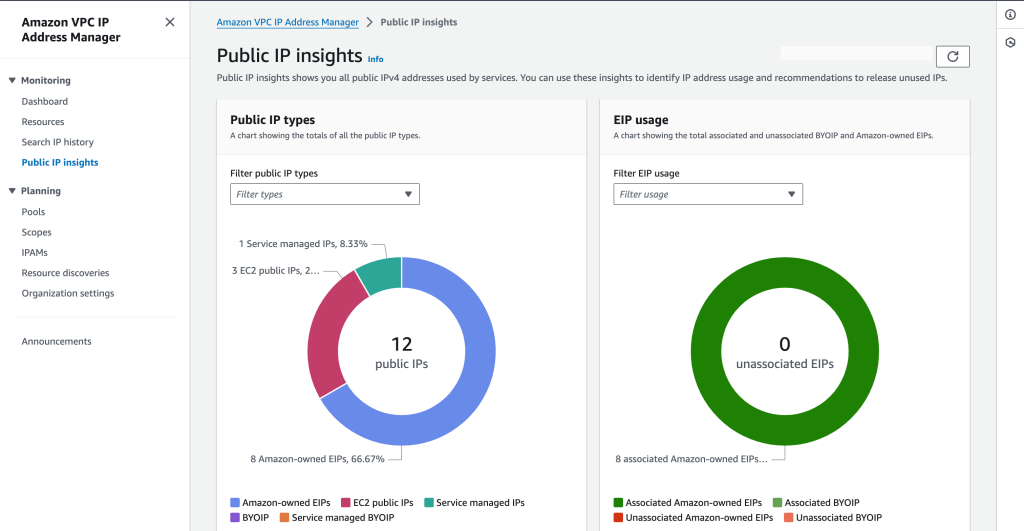
- From the left menu, select “Public IP insights.”
- Allow some time for data to update (it might take a few minutes).
Once complete, you’ll see an overview of your public IPv4 addresses and Elastic IP addresses, providing valuable insights:
- Identify Underutilized Resources: Look for addresses rarely used or belonging to inactive services. These prime candidates for cost-saving actions.
- Consider Private Alternatives: Many applications can function perfectly with private IPv4 addresses within your VPC, eliminating public IP charges.
- Explore IPv6 Adoption: AWS offers free IPv6 addresses, providing a future-proof and cost-effective alternative.
IPV6 Limitations
While IPv6 offers significant benefits for future-proofing your cloud architecture and optimizing costs, it’s important to be aware of current limitations with certain AWS services:
Limited Connectivity:
- VPN Connections: Currently, site-to-site VPN connections and customer gateways do not support IPv6 traffic. However, IPv6 connectivity is possible with Transit Gateway-based VPN connections.
- NAT Devices: NAT gateways for IPv6 are not yet available.
Endpoint Restrictions:
- VPC Endpoints: Direct access to internal services using IPv6 isn’t possible through VPC endpoints.
- Amazon-Provided DNS Hostnames: These currently lack IPv6 support.
EKS Considerations:
- Dual Stack Mode: Assigning both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses to Pods simultaneously within EKS is not yet supported.
- Windows Support: IPv6 compatibility is limited for Windows Pods and services in EKS.
- AWS Load Balancer Controller: This only allows IPv6 traffic for IP targets, excluding hostname-based targeting.
Moving Forward:
Despite these limitations, AWS is actively working on expanding IPv6 support across its services. By understanding these limitations, you can effectively plan your IPv6 adoption strategy and leverage its advantages where possible, while considering alternative solutions for unsupported areas.
This reframed text offers a more informative and balanced approach, highlighting limitations without discouraging IPv6 adoption. It also emphasizes AWS’s ongoing efforts and suggests alternative solutions.
Additional Tips:
- Regularly review your IPAM dashboard to identify new underutilized resources.
- Leverage AWS documentation and community resources for advanced IPAM strategies.
- Consider seeking expert assistance for complex cost optimization scenarios.
By following these steps and tips, you can effectively map and manage your IPv4 resources, optimize your AWS costs, and pave the way for a more efficient and cost-effective cloud infrastructure.
Author: Arik Goldshtein - Devops, Automation and Solutions Architecture Consultant Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/in/arik-goldshtein/